- Protease
- >
- Recombinant Proteinase K
Recombinant Proteinase K
SKU:
$99.00
99
369
$99.00 - $369.00
Unavailable
per item
Products forms: both liquid and lyophilized
Pack sizes: 100 KU, 250 KU and 500 KU
Storage: -20 °C
Molecular weight: 28.9 kDa
Source: Yeast
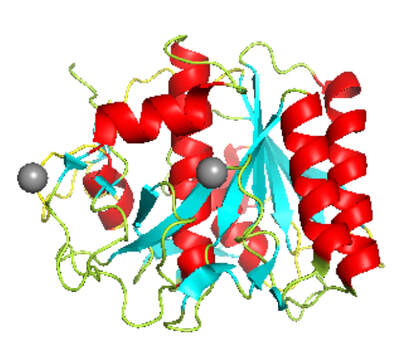
Proteinase K (EC: 3.4.21.64) is a broad-spectrum serine protease. It hydrolyzes the peptide bonds at the cabonyls adjacent to hydrophobic amino acids with aliphatic and aromatic side chains. Therefore, it is often used to clean up enzymatic reactions or cell lysates in nucleic acid preparations. Proteinase K originated from the fungus Tritirachium album Limber. It is used for the destruction of nucleases in cell lysates and for the release of nucleic acids since it very effectively inactivates DNase and RNase. It has two Ca 2+ ions which tighten the loop region and stabilize the protein structure. Proteinase K is stable over a wide range of pH (4–12) with a pH optimum of around pH 8.0 and partially denatured states like in the presence of up to 2% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) or up to 3 M of guanidinium chloride (3 M), and up to 4 M of urea (4 M). The denatured conditions enhance proteinase K activity by making its substrate cleavage sites more accessible. The molecular weight of Proteinase K is 28.9 kDa.
Applications:
Technical Notes:
Applications:
- Digesting proteins and remove contamination in the preparations of nucleic acids by proteinase K makes it very useful for a variety of applications including:
- Rapidly inactivating and cleaving DNase and RNase while isolating DNA and RNA from tissue or cell lysates
- Inactivating RNase, DNase and enzymes after reactions
- Digesting enzymes from DNA to improve cloning efficiency
- Cleaning up PCR product
Technical Notes:
- No detectable endonuclease, exonuclease, DNase or RNase contaminating activities.
- The recommended working concentration of Proteinase K is 0.05 to 1 mg/mL at 50- 60 °C and at pH between 7.5 or 8 with up to 1% SDS and up to 4 M urea.
- Storage Conditions: 20 mM Tris-HCl pH at 7.5 with 5 mM CaCl2 in 50% Glycerol
- Unit Definition: One unit will digest urea-denatured hemoglobin at 37°C (pH 7.5) per minute to produce equal absorbance as 1.0 µmol Ltyrosine using Folin & Ciocalteu's phenol reagent.